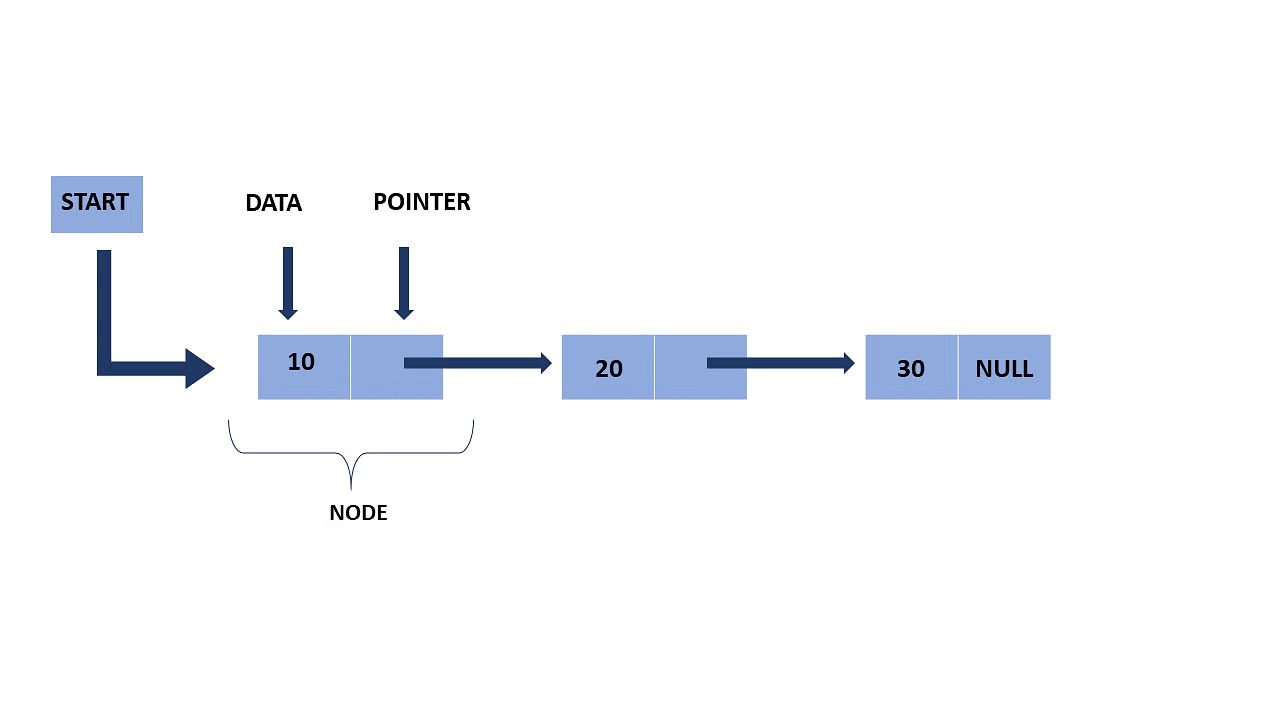
Slow and fast pointer technique for problems involving Linked List or arrays
Hey guys,
Let’s hop into this one, I am excited about the slow and fast pointer because it was the first technique I learned.
Linked List pic above*
Concept: The Fast & Slow Pointer technique involves two pointers moving through the data structure at different speeds. Typically, the "fast" pointer moves twice as fast as the "slow" pointer. This method is useful in detecting cycles, finding the middle of a linked list, or determining if a palindrome(a word or phrase that is the same forwards and backward) can be formed.
Use Case - Detecting Cycles: Imagine you have a linked list. If there is a cycle (a loop in the list), the fast pointer, which moves two nodes at a time, will eventually meet the slow pointer, which moves one node at a time. If they meet, you can confirm there's a cycle. If the fast pointer reaches the end of the list (null), there's no cycle.
Use Case - Finding the Middle Element: In a linked list, if you move the fast pointer two steps for every one step of the slow pointer, when the fast pointer reaches the end of the list, the slow pointer will be at the midpoint. This is handy for problems like finding the middle element of a list without knowing its length upfront.
Use Case - Checking for Palindrome: You can use this technique to find the midpoint of the list, then reverse the second half of the list and compare it with the first half to check if the linked list forms a palindrome.
Leetcode problem using this technique:
Middle of the Linked List
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list. If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [3,4,5]
Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3.Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [4,5,6]
Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 100].
1 <= Node.val <= 100Here’s how I solved it:
class MyListNode {
val: number;
next: MyListNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, next?: MyListNode | null) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val);
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next);
}
}
function middleNode(head: MyListNode | null): MyListNode | null {
let slow: MyListNode | null = head;
let fast: MyListNode | null = head;
// Traverse the list with slow and fast pointers
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow!.next; // move slow pointer by one node
fast = fast.next.next; // move fast pointer by two nodes
}
// When fast pointer reaches the end, slow will be at the middle node
return slow;
}The
slowandfastpointers start at the head of the list.In each loop iteration,
slowmoves one node forward, andfastmoves two nodes forward.When
fastreaches the end of the list (eitherfastbecomesnullorfast.nextbecomesnullin case of an even number of nodes),slowwill be at the middle node.We then return the
slowpointer, which now points to the middle of the list.
Thanks!